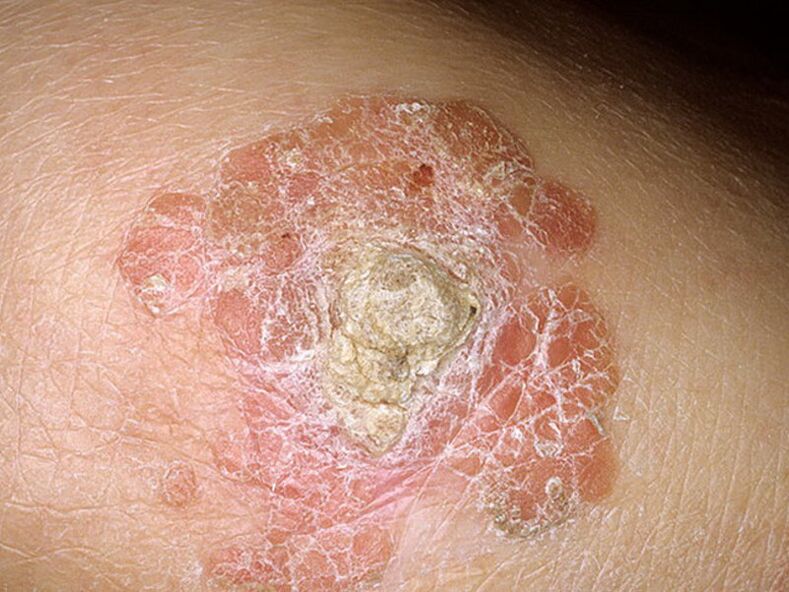
Papilloma virus is a group of viruses with about 24 subgroups. About 600 species have been found so far. It is only transmitted from person to person. Many people and doctors face the problem of diagnosing and treating human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is able to stimulate tumor processes, it is found on the skin, esophagus, oral mucosa, bronchi, conjunctiva and even the rectum.
Causes and types of infection
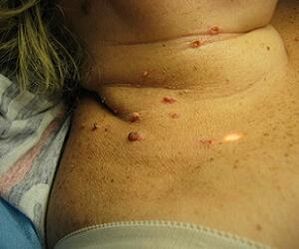
The human papillomavirus is a very common disease transmitted by:
- during sexual intercourse;
- when touched, kissed;
- scratches or cuts when visiting a pool, sauna, public restroom or gym;
- during shaving or epilation.
Statistics show that even with one partner, women become infected in 20% of cases.
About 70% of the population is ill and carries HPV. The virus is particularly active in patients who have warts on the body (the virus causes them to appear) in the form of sharp or flat uneven growths on the skin and genitals. In medicine they are called warts and papillomas.
Newborns can be infected from the mother during childbirth. In infants, the disease manifests as growths in the throat or genitals.
Symptoms and development of the virus
The latency of the disease (incubation) can last from two weeks to several years. There are currently no visible signs of the virus.
Warts can appear on the skin gradually and one at a time, but it is also possible that many warts or papillomas grow rapidly at once, similar in shape to seaweed.
If the infection is sexual, the human papilloma virus affects women:
- pubic lip area;
- vagina;
- cervix;
For men:
- around the head of the penis;
- on the skin of the genitals.
When the partners are fascinated by oral sex, the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat are touched, and for lovers of anal sex - the anus and rectum.
Men rarely suffer from the disease, although they may be carriers. When the spouses are tested, the virus is more common in women.
Attention!If suspicious lesions are found, a doctor should be consulted immediately, as some types of viruses regenerate to cause cancer.
Classification and types
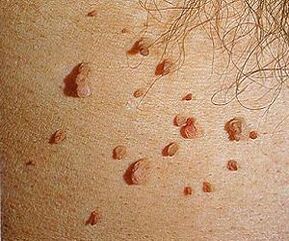
About 600 types of the virus have been detected so far. They are generally harmless and disappear within two years of infection in the presence of normal immunity.
However, about 40 species are dangerous to humans, causing both benign and oncological neoplasms.
In the 1980s, doctors proved a link between HPV infection and cervical cancer.
The following types of viruses are classified according to the location and variety of skin lesions:
- plantar;
- "butcher's warts";
- ordinary;
- flat.
On the genitals:
- genital warts;
- flat, provoking changes in the surface of the cervical membrane and causing oncology;
- papillomas, which cause cancer of the genitals and anus in both women and men.
Other types:
- lesions of the oral mucosa;
- respiratory papillomas;
- neck, head, lung tumors.
Varieties:
- Simple papillomas appear on the back of the palms and can grow on the knees in children. They look like rough cones in the form of cones.
- Plantar - interferes with walking, at first look like shiny growths, then grows to a wart with a border at the base. As they grow, they form a whole pile of similar formations.
- Flat - the color is slightly different from the skin, but causes itching, redness, discomfort.
- Filiforms. In medicine, they are called acrochords. They are more common in people over 50 years of age. At first they look like yellow bumps, grow, form growths up to 6 mm.
When warts appear in visible places, a sick person can go to a medical facility for diagnosis and treatment. It is more difficult to determine the defeat of the cervix or vagina, especially if women do not follow the gynecologist's visits.
Virus diagnostics
If suspicious lesions appear on the skin or mucous membranes in the form of papillary (warty) or uneven, bumpy warts, be sure to consult a doctor. Warts do not cause cancer as often as flat papillomas, but they are best removed to reduce the chance of infecting others.
Given the possibility of developing cancer, such neoplasms are being investigated.
The doctor will perform an analysis of the human papillomavirus - by scraping from the surface of the mucous membrane (colposcopy with damage to the cervix - by examining the mucous membrane with a large enlargement) or skin. The sample is examined under a microscope for changes in tissue structure (dysplasia) and the type of virus.
According to the results of cytological examination, cervical smears are divided into 5 classes:
- no changes;
- changes caused by inflammatory processes;
- there are small changes in the cell structure, histology is required;
- cells with signs of malignancy have been identified;
- there are many cells with signs of cancer.
Histological examination provides a more detailed picture of changes in tissue structure.
Clinics use special HPV tests to obtain more accurate test results. A positive test result indicates the development of malignant processes in the tissues.
HPV is at high risk for oncogenes. High risk of cancer is caused by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18, which have been found in 70% of cases.
Based on the test results, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
HPV treatment methods
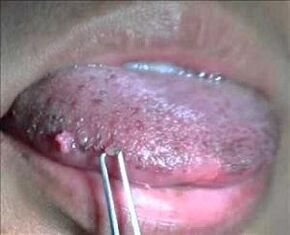
How to treat human papillomavirus? In connection with the reduction of immunity caused by the disease, doctors first prescribe medicines that increase it:
- interferons;
- interferonogens.
But the main treatment is the mandatory removal of neoplasms by modern cosmetology methods:
- diathermic electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction ("cauterization" with liquid nitrogen);
- laser removal;
- radio or chemical treatment;
- administration of immunostimulants or immunomodulators to growths.
In each case, the treatment should be determined by a specialist.
If, according to the test results, pathological processes in the skin are not detected, then only papillomas with a small area around the skin are removed. If malignant cells are detected, the operation can cover a significant area depending on the depth of the lesion.
Folk methods and recipes
How to cure human papilloma virus? Traditional medicine has always helped fight disease. Experience in the treatment of HPV is also quite extensive.
Remedies recommended by traditional medicine. You can lubricate the warts:
- celandine juice;
- sour apples and their juice;
- dandelion juice;
- ammonia.
Proven recipes:
- Prepare chaga, celandine, string infusion, freeze and apply ice cubes 3-4 times a day.
- Lubricate with castor oil, then cover with a cloth. 5-6 such procedures are usually sufficient.
- Kerosene and walnuts. Unripe nuts are chopped in a meat grinder, then mix: 1 part nuts - 2 parts kerosene, the mixture should be poured for three weeks. Apply to the wart 2 times a day.
To increase immunity, herbalists recommend drinking
- potato juice
- echinacea infusion
- rosehip tea.
Drug collections:
- dandelion roots, nettle, lemon balm, horsetail, plantain;
- wormwood, St. John's wort, tricolor violet, dill (seeds), calamus (roots), clover (flowers), plantain.
HPV treatment at home
You can remove papillomas at home using pharmacies:
- A special composition that freezes warts. It should be applied carefully so that it does not get on healthy skin. After the procedure, in about a week, the growths will disappear without leaving any traces.
- Treatment with adhesive tapes. It only takes 3 hours. But it can cause discomfort or pain when it is torn off.
- 2, 5 grams of aspirin powder, the same amount of iodine, 2 grams of boric acid diluted in 100 ml of alcohol and smeared with papillomas.
Infection prevention
And yet do not forget about the nature of the appearance of unpleasant growths viruses. Removing papillomas from the surface of the skin will not get rid of the disease. Therefore, you should visit a specialist to prevent tumor degeneration into cancer. It is not yet possible to completely cure HPV, but you can take steps to avoid getting infected.
Prevention requires:
- use condoms for casual sex. A condom does not completely protect against HPV infection, as it does not cover the entire surface of the skin from contact, but still helps to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Avoid visiting baths, pools, toilets with even the smallest wounds on the skin.
- Children are vaccinated against cervical cancer caused by the HPV virus. 11-12 year old girls are vaccinated. The results of the vaccination showed a reduction in the disease in women who received the medicine.
Have you found a wart or suspicious growth on your body? Contact a competent specialist and follow all recommendations. HPV can sometimes be very dangerous. Learn about treatment and removal methods and take action!














































































